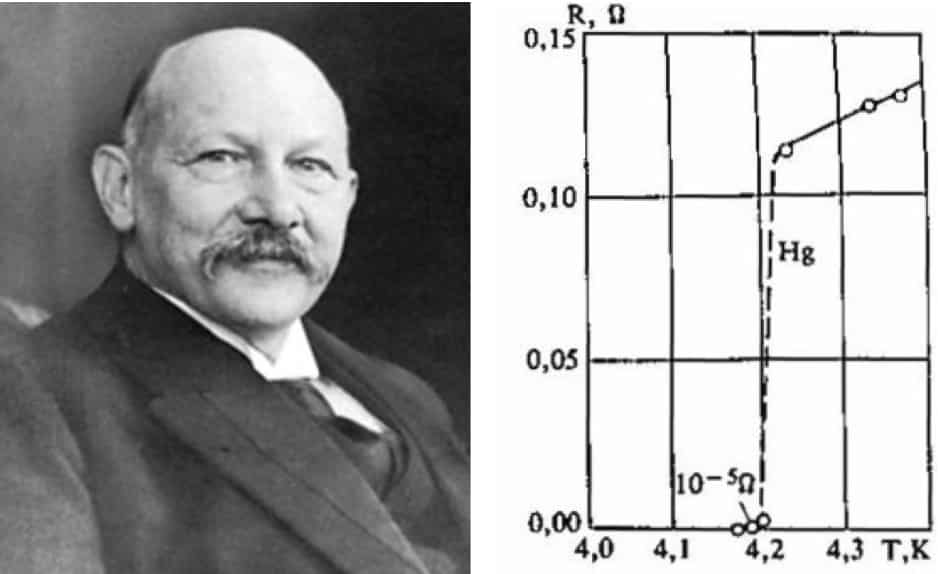
Certain materials, upon cooling below a certain temperature (aka the ‘critical temperature’ or Tc) lose their electrical resistance completely. The phenomena was discovered in 1910 by a Dutch physicist named Heike Kamerlingh Onnes who measured the resistance of Mercury at low temperatures. He noticed a sudden drop in the resistance below a certain temperature and (boldly) claimed to have found a new state of matter, which was later named ‘Superconductivity’.
The reason that scientists were and still are, so excited about superconductivity is the fact that having zero electrical resistance (or infinite conductivity) means that electric/magnetic energy is never lost in these materials. Drive a certain current in a superconducting loop and it will continue circulating forever. Such dissipation-less phenomenon is never seen in the classical world around us. There is always friction and some energy is lost to heat, mechanical movement, distortion, etc.